In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer needs, traditional problem-solving approaches often fall short. Enter design thinking—a powerful methodology that has revolutionized innovation across industries. At its core, design thinking is more than just a process; it’s a mindset, a human-centered approach to problem-solving that fosters creativity and empathy.
What is Design Thinking?
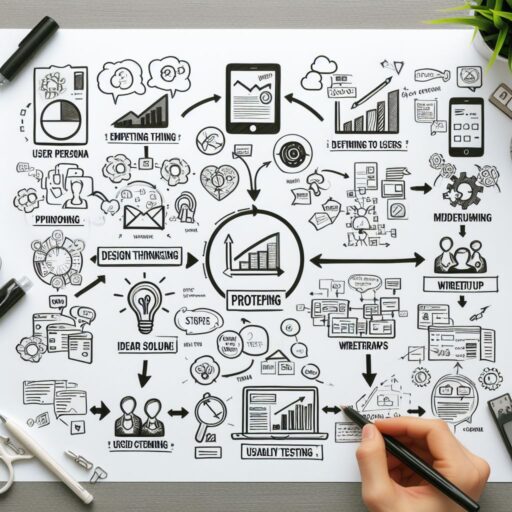
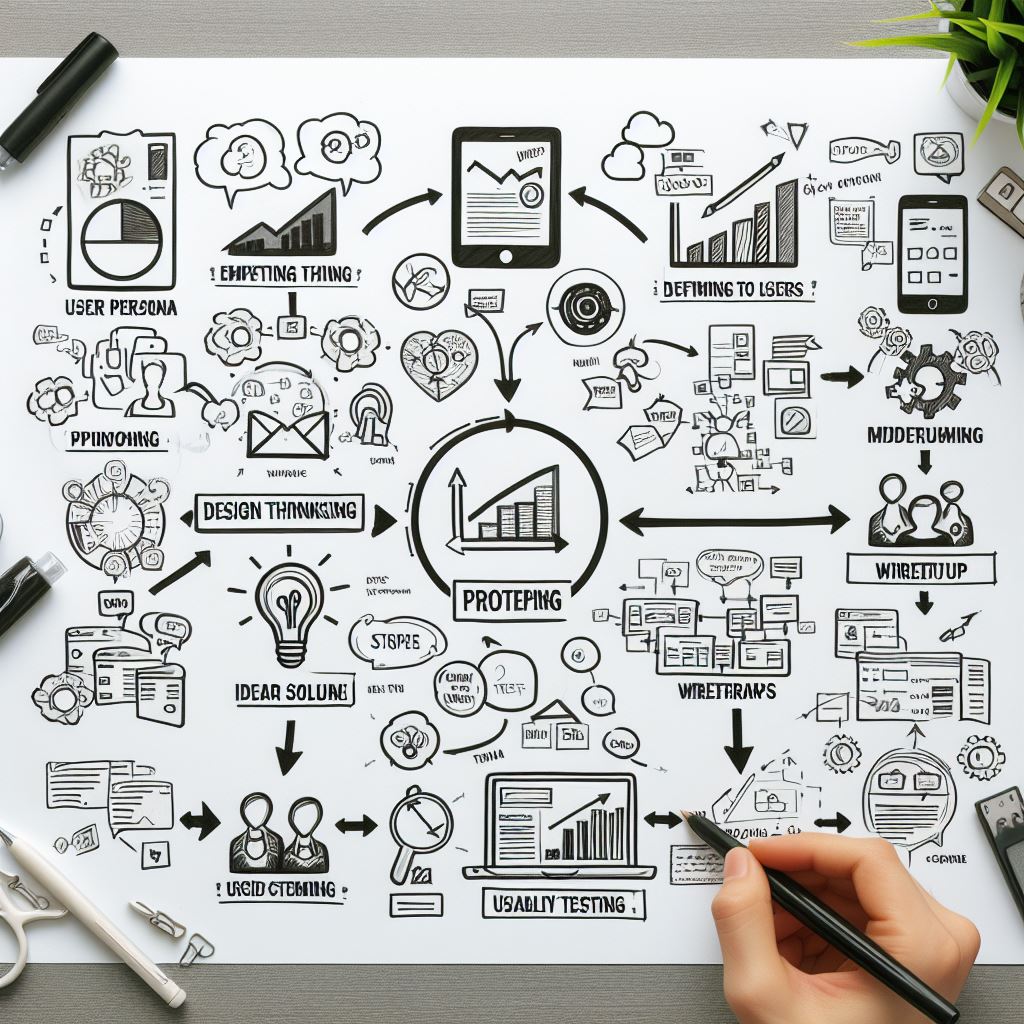
Design thinking is a strategic, iterative process that prioritizes understanding the needs of end-users to create innovative solutions. Unlike linear problem-solving methods, it’s a non-linear, iterative approach that encompasses five key stages:
- Empathize: The process begins by deeply understanding the users’ perspectives, needs, and challenges. Empathy is the cornerstone, enabling designers to see the world through the users’ eyes.
- Define: This stage involves synthesizing gathered information to define the core problems and insights identified during the empathizing phase. It sets the foundation for further ideation.
- Ideate: Here, brainstorming sessions take place, encouraging diverse thinking to generate a wide array of potential solutions. It’s about quantity over quality at this stage, encouraging wild ideas without limitations.
- Prototype: Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas into tangible, testable representations. These can be rough sketches, wireframes, or even functional models, allowing quick and inexpensive validation of concepts.
- Test: Ideas are put to the test through user feedback. This stage helps in refining solutions based on real-world user experiences, leading to further iterations or improvements.
Core Principles of Design Thinking
- Human-Centered Approach: Design thinking prioritizes understanding human needs and experiences, ensuring solutions are tailored to address these.
- Iterative Process: The process is not linear; it encourages continuous refinement and iteration based on feedback.
- Collaborative Environment: It thrives on multidisciplinary collaboration, incorporating diverse perspectives to foster innovative solutions.
Applications of Design Thinking
Design thinking transcends industries and has found application in various domains:
- Product Design: Creating user-friendly products that resonate with consumers.
- Service Design: Designing seamless customer experiences.
- Business Strategy: Developing innovative business models and strategies.
- Education: Reforming educational approaches to meet diverse learning needs.
- Healthcare: Enhancing patient-centric care and improving medical processes.
Benefits of Design Thinking
- Enhanced Innovation: Encourages out-of-the-box thinking and fosters a culture of innovation.
- Improved User Experience: Solutions are tailored to meet user needs, resulting in higher satisfaction.
- Problem-Solving Agility: Adaptable approach to solving complex problems.
- Increased Collaboration: Encourages cross-functional collaboration and empathy among team members.
Conclusion
Design thinking is more than just a process; it’s a mindset that empowers individuals and organizations to innovate and solve problems creatively. Embracing empathy, iteration, and collaboration, it has become a guiding philosophy for those seeking impactful and human-centered solutions in a rapidly changing world.