IoT stands for Internet of Things. It refers to the interconnectedness of physical devices, such as appliances and vehicles, that are embedded with software, sensors, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data. This technology allows for the collection and sharing of data from a vast network of devices, creating opportunities for more efficient and automated systems.
In the upcoming years, IoT-based technology will offer advanced levels of services and practically change the way people lead their daily lives. Advancements in medicine, power, agriculture, smart cities, and smart homes are just a few of the categorical examples where IoT is strongly established.
Key components of IoT include:
- Devices/Things: These are the physical objects or devices that are embedded with sensors, actuators, and connectivity to collect and exchange data. Examples include smart thermostats, wearable devices, industrial sensors, and more.
- Connectivity: The devices in an IoT system need to be connected to the internet or other communication networks to enable data exchange. This can be achieved through various communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, cellular networks, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and more.
- Data Processing: Collected data is processed locally on the device or sent to a cloud server for analysis. This involves converting raw data into meaningful information that can be used for decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms play a crucial role in IoT by providing storage, processing power, and data analysis capabilities. Cloud services help manage and analyze the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices.
- Data Security: Ensuring the security of data transmitted and stored by IoT devices is a critical aspect. Security measures include encryption, authentication, and secure protocols to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing the collected data can provide valuable insights and enable better decision-making. Predictive analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are often employed to derive meaningful patterns and trends from IoT data.
- Applications: IoT has diverse applications across various industries, including smart homes, healthcare, agriculture, industrial automation, smart cities, and more. It enhances efficiency, improves resource management, and enables new services and business models.
- Standards and Protocols: Standardization is essential for interoperability among different IoT devices and systems. Common protocols and standards, such as MQTT, CoAP, and others, facilitate seamless communication between devices from different manufacturers.
Working of Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices usually have some form of built-in intelligence, which allows them to gather data and make decisions without human intervention. Following are the general working principles of IoT.
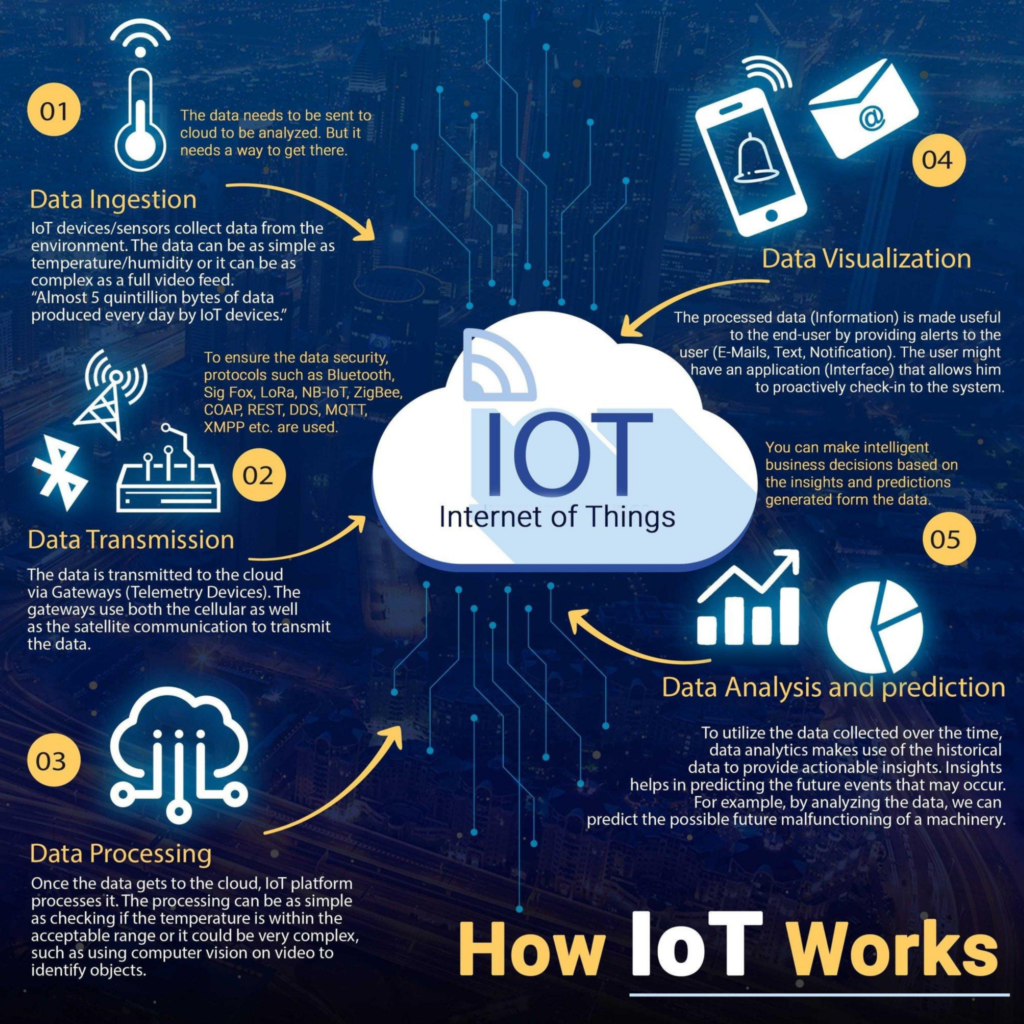
Data Ingestion: IoT devices or sensors collect data from the environment and provide inputs such as temperature and humidity for further processing in clouds.
Data transmission: The data is transmitted to the cloud via Gateway. Gateway uses both cellular and satellite communication to transmit data.
Data processing: Data processed at cloud level generates optimal response. For example, to check the temperature range of an Air Conditioner.
Data visualization: It is about showing information and alerting for proactive response.
Data analysis and prediction: Data analytics make use of collected data over time to provide actionable insight. It helps in predicting future events.
For example, by analyzing data, future malfunctioning of machines can be predicted.
IoT applications
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, IoT devices can be used to monitor patients remotely and collect real-time data on their vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen saturation. This sensor data can be analyzed to detect patterns and identify potential health issues before they become more serious. IoT devices can also be used to track medical equipment, manage inventory and monitor medication compliance.
Manufacturing
Industrial IoT devices can be used in manufacturing to monitor machine performance, detect equipment failures and optimize production processes. For example, sensors can be used to monitor the temperature and humidity in an manufacturing facility, ensuring that conditions are optimal for the production of sensitive products. IoT devices can also be used to track inventory, manage supply chains and monitor the quality of finished products. Industrial IoT is such an expansive new technology space, that it is sometimes referred to by its own abbreviation: IIoT (Industrial IoT).
Agriculture
IoT devices can be used in agriculture to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns and crop growth. For example, sensors can be used to measure the moisture content of soil, ensuring that crops are irrigated at the optimal time. IoT devices can also be used to monitor livestock health, track equipment and manage supply chains. Low-power or solar-powered devices can often be used with minimal oversight in remote locations.
Retail
In the retail industry, IoT devices can be used to track customer behavior, monitor inventory levels and optimize store layouts. For example, sensors can be used to track foot traffic in a store and analyze customer behavior, allowing retailers to optimize product placement and improve the customer experience. IoT devices can also be used to monitor supply chains, track shipments and manage inventory levels.
Smart Cities
Cities can be made more efficient so that they require fewer resources and are more energy-efficient. This can be done with a combination of sensors in different capacities all over the city that can be used for various tasks ranging from managing the traffic, controlling handling waste management, creating smart buildings, optimizing streetlights, etc. There are many cities in the world that are working on incorporating IoT and becoming smarter such as Singapore, Geneva, Zurich, Oslo, etc. One example of creating smart cities is the Smart Nation Sensor Platform used by Singapore which is believed to be the smartest city in the world. This platform integrates various facets of transportation, streetlights, public safety, urban planning, etc. using sensors in conjugation with IoT.







